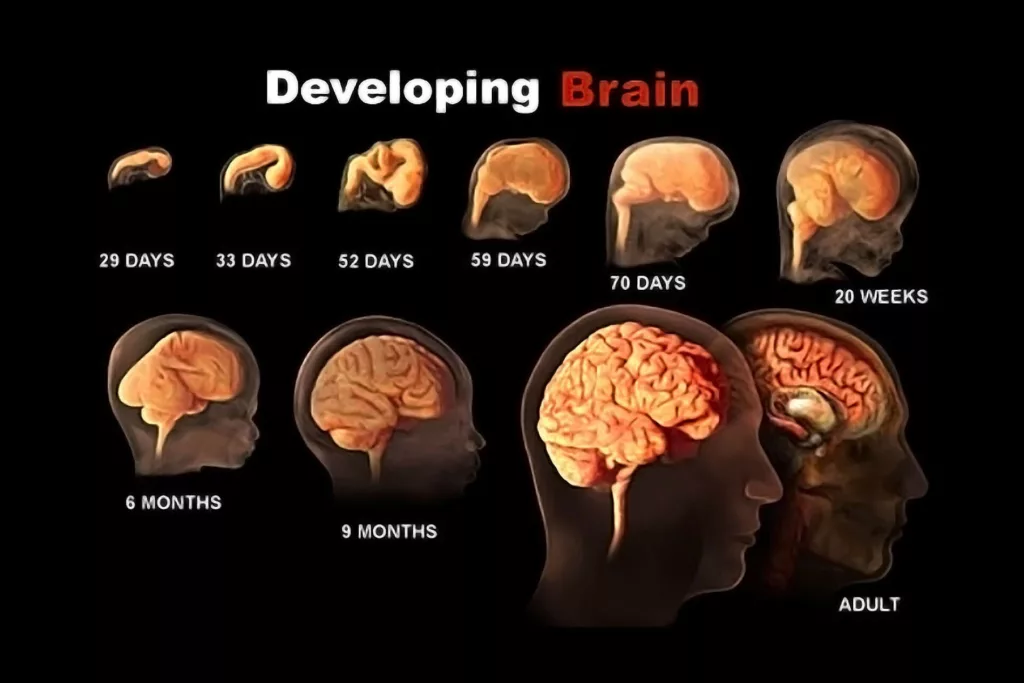
The Importance of Early Brain Development
Brain development begins before birth and continues rapidly during the early years of life. In fact, the first few years are crucial for laying the foundation of cognitive, emotional, and social skills.
Moreover, the brain forms new connections at a rapid rate during this time. Early experiences, whether positive or negative, significantly shape a child’s brain structure and function.
The First Year: The Foundations of Growth
In the first year, a baby’s brain undergoes rapid development. At birth, the brain is already capable of basic functions like breathing, moving, and reacting to stimuli.
However, it is during this period that sensory experiences, such as touch, sight, and sound, play a major role in shaping brain growth. Babies begin to make important neural connections as they engage with caregivers, explore their environment, and learn from these experiences.

The Toddler Years: Language and Social Skills
From one to three years, toddlers experience a significant increase in brain activity, particularly in areas related to language, memory, and social interactions.
By this stage, children are rapidly developing their vocabulary and understanding the world around them. Interaction with caregivers, especially through conversations and reading, helps strengthen language skills and supports cognitive development. Furthermore, toddlers start to exhibit basic social skills, such as recognizing emotions and understanding the concept of sharing.
Early Childhood: Problem-Solving and Emotional Growth
Between ages three and six, the brain continues to develop at an impressive pace, with an increasing focus on problem-solving and emotional regulation.
During this period, children learn to engage in imaginative play, which promotes creativity and cognitive flexibility. Additionally, emotional development is crucial. Children begin to recognize and manage their emotions and start developing empathy for others. Positive experiences, like supportive relationships and engaging activities, help foster a sense of security, which is essential for emotional growth.
School-Age Years: Refining Cognitive Skills
By the time children reach school age (6-12 years), their brains are refining the skills learned in early childhood. Areas of the brain involved in logical thinking, attention, and memory become more active.
This is the period when children start developing a stronger sense of academic skills like reading, writing, and math. Additionally, social interactions become more complex, as children learn to navigate friendships and group dynamics. They also begin to develop a sense of independence and personal identity.
The Teen Years: Brain Maturity and Decision-Making
Teenagers undergo another crucial phase of brain development. While the brain continues to grow, it is the maturation of the prefrontal cortex that becomes most significant during these years.
The prefrontal cortex is responsible for decision-making, impulse control, and planning. This is why adolescents often take risks or make impulsive decisions, as their brains are still fine-tuning these areas. As they mature, they gain more control over emotions, behavior, and decision-making.
The Role of Experience in Brain Development
Experience plays a fundamental role in shaping brain development. Positive, nurturing environments that encourage exploration, learning, and emotional connection strengthen the brain’s neural pathways.
On the other hand, negative experiences such as chronic stress, neglect, or trauma can disrupt brain development, leading to potential cognitive and emotional challenges later in life. Hence, early intervention and support are key to ensuring healthy brain growth.
The Impact of Play on Brain Development
Play is essential for brain development at every stage. Through play, children learn to explore their environment, solve problems, and express their emotions.
In addition, play helps develop motor skills, social understanding, and cognitive flexibility. Whether it’s building blocks, puzzles, or outdoor games, play provides critical opportunities for brain stimulation and learning.
Nutrition and Brain Health
A healthy diet is another vital factor influencing brain development. Proper nutrition, especially in the early years, ensures the brain receives the necessary nutrients to grow and function effectively.
Nutrients like omega-3 fatty acids, iron, and vitamins play a key role in supporting cognitive development, while deficiencies in these nutrients can result in cognitive delays or difficulties.
Conclusion
Understanding brain development in children highlights the importance of early experiences in shaping a child’s cognitive, emotional, and social abilities. From birth through adolescence, the brain undergoes significant changes that are influenced by interactions, experiences, and environmental factors.
By providing a nurturing environment, encouraging positive interactions, and offering enriching activities, we can help children develop the skills and resilience needed for a healthy future.